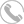Written By Rich Jiang On 8th November 2022
NFC is called Near Field Communication, which supports short-range communication between compatible devices. It requires at least one transmission device, and one receiving signal. A range of devices can use the NFC standard, and will be considered passive or active.
There are two main types of NFC devices - passive NFC devices and active NFC devices. Passive NFC devices include NFC tags and other small transmitters that can send information to other NFC devices without the need for power. However, they cannot process information from other sources and cannot connect to other passive devices.
Active NFC devices can send and receive data and can communicate with each other and with passive devices. Currently, smartphones are the most common active NFC devices, and other common examples include bus readers on self kiosks and payment terminal on self touch kiosks.

How NFC Works?
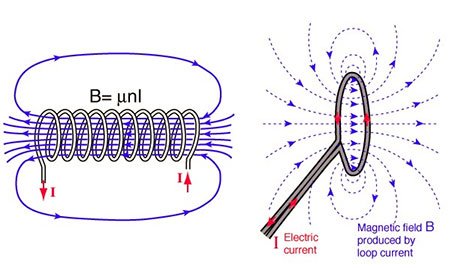
Now that we know what NFC is, how does it work? Just like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and various other wireless communication technologies, NFC works by sending information through radio waves, which is also a standard for wireless data transmission. This means that devices must adhere to a specific specification in order to properly communicate with each other. The technology used in NFC is based on the evolution of the older contact-free radio frequency identification (RFID), which uses electromagnetic induction to transmit information and is backward compatible with RFID.
This is one of the main differences between NFC and Bluetooth/WiFi. NFC uses the principle of electromagnetic induction, where an active NFC element can sense current and send data in a passive element. This means that passive devices do not need their own power source, and they can be powered by the electromagnetic field generated by the active NFC component when it comes into communication range. However, NFC technology does not have enough sensing power to charge our smartphones, but QI wireless charging is based on the same principle.
The operating frequency of NFC is 13.56MHz, the distance is within 10cm, and its transmission speed is 106Kbit/sec, 212Kbit/sec or 424Kbit/sec. This transmission speed is sufficient for transferring files such as pictures and music.
Application
To determine what type of information will be exchanged between devices, the NFC standard currently has three different modes of operation: point-to-point, reader-writer, and card emulation.
Smartphones are most commonly used in point-to-point mode, which allows two nfc-enabled devices to exchange various information with each other. In this mode, the two devices switch between active and passive when sending data and receiving data.
Reader mode is a one-way data transfer. In this mode, the NFC-enabled phone collects data from the TAG and processes it according to the requirements of the application; NFC advertising tags and access cards on self kiosks use this mode.
The last mode of operation is the card simulation mode. In this application mode, the NFC reading device collects data from the TAG-capable NFC phone, and then sends the data to the application processing system for processing through the wireless transmitter function. Typical applications based on this mode include mobile payment on all-in-one kiosk machines, taking public transportation and subway, etc.

Comparison Of NFC And Bluetooth
So, how does NFC compare to other wireless technologies? Considering that Bluetooth has been popular for a long time, we believe that some people may think that NFC is not necessary for its existence. However, there are several important technical differences between the two, which give NFC some significant advantages in certain situations. one of the major advantages of NFC over Bluetooth is that it consumes less power, which makes NFC ideal for use as passive devices, such as the aforementioned advertising tags, because they can operate without power.
However, there are two sides to the coin, and NFC's low power consumption also brings with it some drawbacks. The most obvious of these is that NFC's transmission distance is much shorter than Bluetooth. As mentioned above, the maximum transmission range of NFC is about 10 cm, while the Bluetooth connection can transmit up to 10 m or more. is 1 Mbit/s.
But NFC has another major advantage: the connection is much faster, and thanks to the inductive coupling technology, it takes less than a tenth of a second to establish a connection between two devices without the need for manual pairing. Although modern Bluetooth connections are already very fast, they are still nowhere near as fast as NFC connections, which are essential for certain scenarios, such as mobile payments.
Summary
While Bluetooth works better for connecting devices together for file transfers, sharing connections with speakers, etc., the CY Digital Signage team believes that NFC technology will always have a place due to the rapid popularity of mobile payments, the Internet of Things, etc.
This is the time to bring your projects to the next level and truly create an impact with a display that is not going to be missed. The digital signage displays are now in stock so GET IN TOUCH TODAY to reserve yours and avoid disappointment!
 Rich Jiang
Rich Jiang
Rich Jiang is the Marketing Director at CY Digital Signage. And he has over 15 years experiences in digital signage displays.